Section 7 Using AI Integrations
In the ROSSyndicate, we are actively trying to use some of the large language models to make our jobs easier/more efficient. AI models can be valuable tools in code development if used effectively. These models can understand and generate human-like text, offering assistance in writing and suggesting code snippets. However, it’s important to note that while they enhance productivity, AI models are currently not a replacement for coding; they should act only as supportive aids. Never take the response of an AI model at face value. AI models are flawed and make mistakes often. Even so, they have the potential of saving you substantial time and can give you a massive boost. With that, here is a list of ways in which AI models can be effectively used to help you on your coding journey.
As you use AI to help with coding, it is best practice to note use of AI in code development. This can be as simple as including the following statement in the README of the repository: “In development of the code in this repository, AI (state what models were used) was used to help debug throughout development, develop documentation, and generally improve existing code.” MR has also made some high-level suggestions that you can include inline or in the README as it seems fit: “Claude wrote the foundational code for this app and then we edited it”, “this figure was generated by Claude 3.7”.
The following section is a modification of a Twitter thread written by Santiago Valdarrama (@Santiago) to provide examples of how you can used AI within the context of code development:
Explaining code. AI model explanations can be very detailed. Dropping convoluted or confusing code into an AI model (plus a request to explain it) can be much quicker than trying to figure out code on your own.
Improving existing code. Asking an AI model to improve existing code by dropping it into the chat-bot plus describing what you want it to accomplish will often result in a response that includes working (or, at least close to working), modified code.
Rewriting code with a different style. For example, it can be great for re-writing code written in base R into {tidyverse}-style code. AI models will not only give you the updated code, they will also explain the reason for the changes they make.
Simplifying code. Asking AI models to simplify complex code can result in a much more compact version of the original code. The output will also provide an explanation for the changes, as well as whether the simpler version is as efficient as the original code.
Debugging. If you are having a hard time finding the source of an error in your code, AI models are a great solution. Just provide it the code, and it will often find it and fix it for you.
Workflow development. Use AI models to kick off the structure of anything new you want to write.
Writing test cases. When writing functions, you can use AI models to generate test cases for you to use in testing whether a function is working the way you want it to.
Exploring alternatives. Asking an AI model what the most efficient way to perform a coding action might teach you new ways of writing more efficient and sophisticated code.
Translating code. Anytime you want to translate some code from one language to another, ask an AI model to help you.
Writing documentation. Ask an AI model to write the documentation for a piece of code, and it usually does a pretty great job. It will often even include usage examples as part of the documentation.
Integrating AI into your workflows:
Below is one of the most sustainable ways to integrate the CoPilot LLM into your workflow. We encourage all members of the lab to sign up for (and use!) any of the following sites:
GitHub CoPilot
7.1 Using GitHub CoPilot in VSCode + RStudio
VSCode also has an extension for GitHub CoPilot, it will auto complete your comments and code in nearly any programming language. By having open both VSCode and RStudio and enabling auto-save in both programs, you can hop between the two programs and code will update between the two as you switch. Big thanks to Sam Struthers for figuring out this integrated workflow.
7.2 Accessing GitHub CoPilot as a student/teacher/researcher
Access to GitHub CoPilot is currently free to students/teachers/researchers. Follow the instructions here to submit an application to gain access to the program: https://education.github.com/discount_requests/pack_application. A screenshot of your ‘employee information’ from the human resources portal will be sufficient information to verify your employment. GitHub usually will give you access to the educational portal within 1 business day.
7.3 Downloading VSCode and installing the GitHub CoPilot extension
Download VSCode here: https://code.visualstudio.com/. Set up the GitHub and GitHub CoPilot extensions by adding them via the ‘Marketplace’. You can bring up the Extensions from the menu bar under ‘Code’, ‘Settings’, ‘Extensions’.
You’ll want to install and activate ‘GitHub Pull Requests and Issues’ as well as ‘GitHub Copilot’. You will be directed to Sign In using your GitHub credentials. You may need to elect to ‘enable’ Copilot.
7.4 Setting up AutoSave in VSCode + RStudio
In RStudio, open the Preferences pane from the menu bar under ‘RStudio’, then find the following pane:
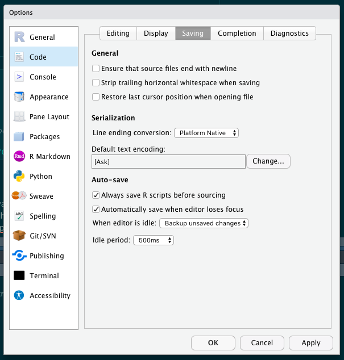
Set up Auto-save by checking the ‘Automatically save when editor loses focus’ and ‘Apply’.
In VSCode, select ‘Code’, ‘Settings’, then ‘Settings’ again from the menu bar to bring up the Settings tab in your console. Then type in ‘auto save’ in the top search bar, and select ‘onFocusChange’ for the ‘Files: Auto Save’ Setting.
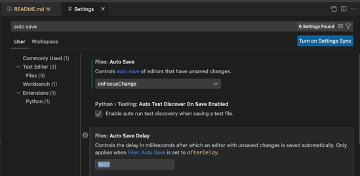
Now you can switch between programs, using VSCode and CoPilot to draft code and comment chunks, then further editing/running in RStudio.